- Published on
Singly Linked List
- Authors

- Name
- Ashley Fernandes
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Advantages of using linked lists
- Disadvantages of using linked lists
- Where are linked lists used
- List of operations on a linked list
- Javascript implementation of a linked list
- Leetcode Linked List problems
- Time / Space Complexity (Worst case)
Introduction
Linked lists are a versatile data structure that can be used in a variety of applications. They are particularly useful for applications where the order of the data is important, and where the data needs to be able to be inserted, deleted, and updated efficiently. 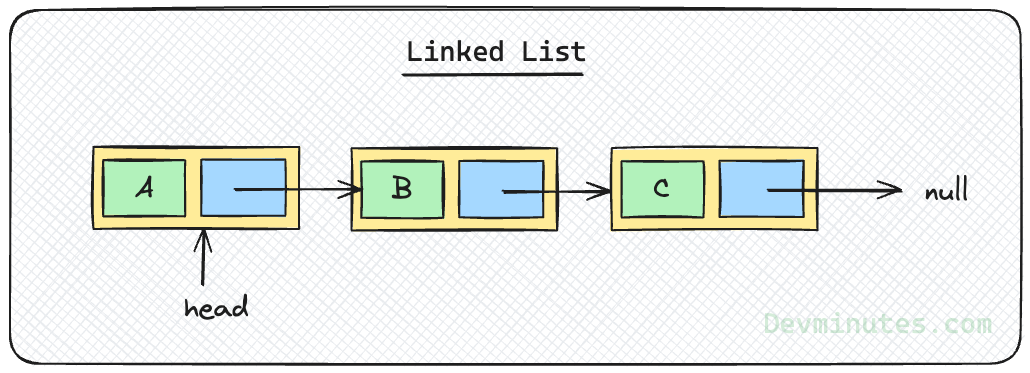

Advantages of using linked lists
- Flexibility: Linked lists can be used to implement a variety of data structures, such as stacks, queues, and deques.
- Efficiency: Linked lists are efficient for inserting and deleting data, as only the pointers need to be updated.
- Simplicity: Linked lists are relatively simple to implement and understand.
Disadvantages of using linked lists
- Memory usage: Linked lists can use more memory than other data structures, such as arrays.
- Complexity: Linked lists can be more complex to traverse than other data structures, such as arrays.
Where are linked lists used
- Databases: use linked lists to implement data structures such as hash tables and adjacency lists for representing relationships between data entities.
- Music players: can use linked lists to implement playlists, allowing for easy insertion, deletion, and traversal of songs.
List of operations on a linked list
- Traversal: This operation involves visiting each node in the list, starting from the head node and ending at the tail node. It is used to print the contents of the list or to search for a specific node in the list.
- Insertion: This operation involves adding a new node to the list. There are three types of insertion: insertion at the beginning, insertion at the end, and insertion at a specific position.
- Deletion: This operation involves removing a node from the list. There are three types of deletion: deletion from the beginning, deletion from the end, and deletion at a specific position.
- Searching: This operation involves finding a specific node in the list. It is usually done by traversing the list and comparing each node's data with the search key.
- Reversing: This operation involves reversing the order of the nodes in the list.
Javascript implementation of a linked list
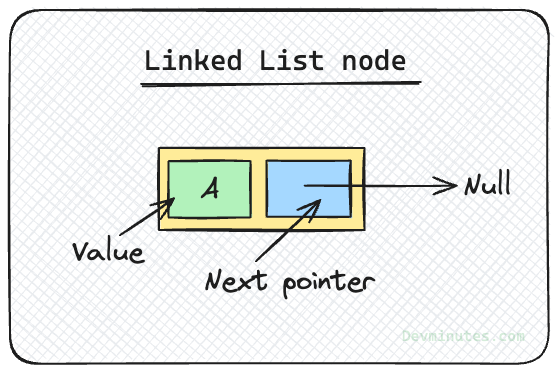
Creating a linked list node
LinkedListNode.js
class LinkedListNode {
constructor(value, next = null) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
Creating the linked list class
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.length = 0;
}
}
Prepend - add a node to the start of the list
prepend(value) {
// Create a new node with the current head as the next pointer
const node = new LinkedListNode(value, this.head);
// Make this new node as the head
this.head = node;
// increase length
this.length++;
return this;
}
Append - add a node to the end of the list
append(value) {
const node = new LinkedListNode(value);
// check if head exists or not
// if it does not exist then this new node becomes the head
if (!this.head) {
this.head = node;
} else {
// if head exists traverse to the end of the list and
while (curr && curr.next) {
curr = curr.next;
}
// add the new node to the end
curr.next = node;
}
this.length++;
return this;
}
Find - insert a node after a given node index
find(value) {
// if head does not exist return null
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}
// traverse the list till value is found
let curr = this.head;
while (curr && curr.value !== value) {
curr = curr.next;
}
return curr ? curr : null;
}
InsertAfter - insert a node after a given node index
insertAfter(value, rawIndex) {
// check for valid index
const index = rawIndex < 0 || !rawIndex ? 0 : rawIndex;
// create new node
const node = new LinkedListNode(value);
// if head does not exist use newly created node as head
if (!this.head) {
this.head = node;
} else {
// use count variable to keep track of the index
let count = 0;
let curr = this.head;
// traverse till the proper index is reached
while (curr && curr.next && count !== index) {
curr = curr.next;
count++;
}
// once current index is found mark
if (curr) {
// new nodes next as current nodes next
node.next = curr.next;
// current nodes next as new node
curr.next = node;
}
}
this.length++;
return this;
}
InsertAt - insert a node at a given node index
insertAt(value, rawIndex) {
// check for valid index
const index = rawIndex < 0 || !rawIndex ? 0 : rawIndex;
// create new node
const node = new LinkedListNode(value);
// if head does not exist use newly created node as head
if (!this.head) {
this.head = node;
} else {
// need to check if current index is first node or head
// so that new head can be assigned
if (index === 0) {
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
} else {
let count = 0;
let curr = this.head;
// traverse till the one position before proper index is reached
while (curr && curr.next && count !== index - 1) {
curr = curr.next;
count++;
}
if (curr) {
// new nodes next as current nodes next
node.next = curr.next;
// current nodes next as new node
curr.next = node;
}
}
}
this.length++;
return this;
}
DeleteHead - delete the head of the linked list and assign a new head
deleteHead() {
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}
const deletedElement = this.head;
this.head = this.head.next;
this.length--;
return deletedElement?.value;
}
DeleteTail - delete the last node of the linked list
deleteTail() {
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}
let curr = this.head;
/* keep track of previous or 2nd last element since this
become the new last element */
let prev = null;
while (curr && curr.next) {
prev = curr;
curr = curr.next;
}
prev.next = null;
this.length--;
return this;
}
Delete - delete a particular node by value
delete(value) {
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}
// if head needs to be deleted
if (this.head.value === value) {
this.deleteHead();
return;
}
let curr = this.head;
/* Traverse till one node before the desired node */
while (curr && curr.next && curr.next.value !== value) {
curr = curr.next;
}
if (curr) {
curr.next = curr.next.next;
}
this.length--;
}
Reverse - Reverse a linked list
reverse() {
let curr = this.head;
let prev = null;
let next = null;
while (curr) {
next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
// since curr will be null prev will be in the
// last postion which becomes the new head
this.head = prev;
return this;
}
Complete code
LinkedList.js
import LinkedListNode from './LinkedListNode';
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.length = 0;
}
prepend(value) {
const node = new LinkedListNode(value, this.head);
this.head = node;
this.length++;
return this;
}
append(value) {
const node = new LinkedListNode(value);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = node;
} else {
let curr = this.head;
while (curr && curr.next) {
curr = curr.next;
}
curr.next = node;
}
this.length++;
return this;
}
insertAfter(value, rawIndex) {
const index = rawIndex < 0 || !rawIndex ? 0 : rawIndex;
const node = new LinkedListNode(value);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = node;
} else {
let count = 0;
let curr = this.head;
while (curr && curr.next && count !== index) {
curr = curr.next;
count++;
}
if (curr) {
node.next = curr.next;
curr.next = node;
}
}
this.length++;
return this;
}
insertAt(value, rawIndex) {
const index = rawIndex < 0 || !rawIndex ? 0 : rawIndex;
const node = new LinkedListNode(value);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = node;
} else {
if (index === 0) {
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
} else {
let count = 0;
let curr = this.head;
while (curr && curr.next && count !== index - 1) {
curr = curr.next;
count++;
}
if (curr) {
node.next = curr.next;
curr.next = node;
}
}
}
this.length++;
return this;
}
delete(value) {
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}
if (this.head.value === value) {
this.deleteHead();
return;
}
let curr = this.head;
while (curr && curr.next && curr.next.value !== value) {
curr = curr.next;
}
if (curr) {
curr.next = curr.next.next;
}
this.length--;
}
deleteHead() {
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}
const deletedElement = this.head;
this.head = this.head.next;
this.length--;
return deletedElement?.value;
}
deleteTail() {
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}
let curr = this.head;
let prev = null;
while (curr && curr.next) {
prev = curr;
curr = curr.next;
}
prev.next = null;
this.length--;
return this;
}
find(value) {
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}
let curr = this.head;
while (curr && curr.value !== value) {
curr = curr.next;
}
return curr ? curr : null;
}
reverse() {
let curr = this.head;
let prev = null;
let next = null;
while (curr) {
next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
this.head = prev;
return this;
}
toArray() {
let start = this.head;
const arr = [];
while (start) {
arr.push(start.value);
start = start.next;
}
return arr;
}
toString() {
return this.toArray().join(' ');
}
}
Usage
const list = new LinkedList();
list.prepend(34);
list.prepend(54);
list.prepend(90);
list.append(66)
list.toString(); // 90 54 34 66
Leetcode Linked List problems
- 206. Reverse Linked List
- 21. Merge Two Sorted Lists
- 141. Linked List Cycle
- 19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
Time / Space Complexity (Worst case)
| Operation | Time complexity | Space complexity |
|---|---|---|
| prepend | O(1) | O(1) |
| append | O(N) | O(1) |
| insertAfter | O(N) | O(1) |
| insertAt | O(N) | O(1) |
| deleteHead | O(1) | O(1) |
| deleteTail | O(N) | O(1) |
| delete | O(N) | O(1) |
| reverse | O(N) | O(1) |
| find | O(N) | O(1) |
